The existence of many contemporary tools and appliances that we take for granted is thanks to the invention, study and application of new materials. As we continue to experiment with metal alloys and neo-compounds, we are able to weaponize new properties to create products and tools that meet new needs.
One of the most impactful inventions in this regard is nichrome. Nichrome is an alloy found in a great many commercial and industrial appliances, but its presence is not commonly known or understood by the layperson. What is it – and how does it work?
What Is Nichrome?
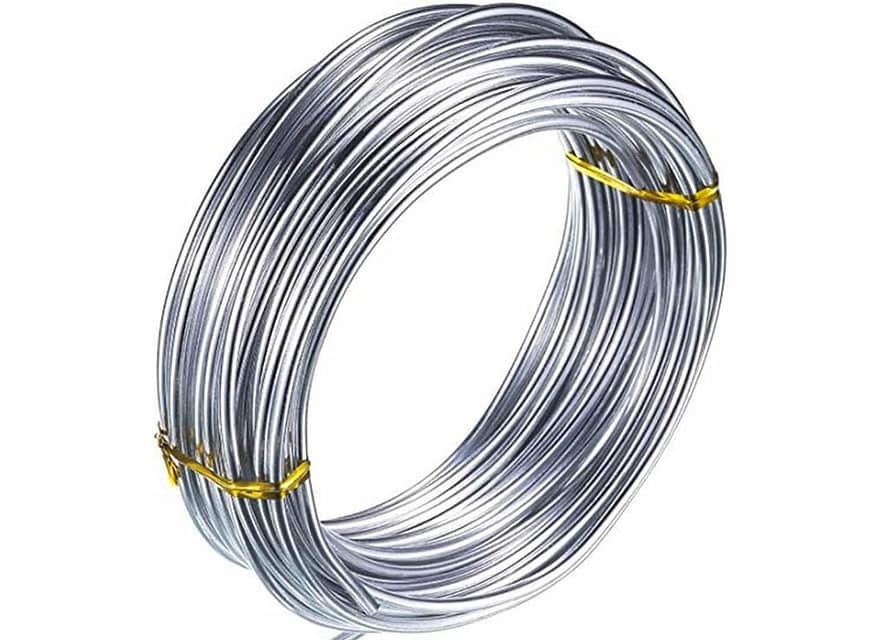
Nichrome describes a family of metal alloys. These alloys contain, in varying quantities, chromium, iron and nickel as core ingredients. Other metals may also be present in minute quantities, depending on the specific purpose of a given nichrome alloy.
Nichrome wire is simply a spooled length of nichrome alloy for use in a variety of industrial and scientific applications. The alloy possesses various innate qualities, which render it perfect for practical utility in electronics, engineering, manufacture and even medicine.
The Properties of Nichrome Wire
Nichrome as an alloy shares the oxidation resistance properties of chrome. Nichrome forms a thin oxide layer on its surface that seals the alloy from further oxidation and corrosion, rendering it fairly inert with regard to contact with moisture or varying pH levels. There are relatively few instances in which corrosion can occur properly, involving high-temperature acids and haloacids.
Nichrome is not only resistant to oxidation and corrosion, but also to heat. Nichrome can withstand temperatures well above 2000 degrees Fahrenheit, depending on the specific ratio of core metals in the alloy. This heat resistance combines with another key property to make nichrome particularly useful industrially: electrical resistance.
As nichrome provides high electrical resistance, heat energy can be generated quickly through the provision of electrical current. The high heat resistance means the nichrome can be electrically induced to heat itself to incredibly high temperatures.
Practical Uses of Nichrome Wire
The above properties make nichrome wire a widely useful component part, with practical applications across industries. It is perhaps most commonly used in laboratories as a form of remote ignition solution, to enable the carrying-out of dangerous experiments without proximal location to the reaction. Nichrome wire can be used to ignite compounds from beyond a fume-box, or at a distance.
Nichrome can also be used as an inert device for transferring samples from one place to another. Nichrome implements can lift biological materials and place them in petri dishes without reacting with the sample or corroding in the process.
Nichrome wire also has a number of commercial applications, being the core heating element that enables the function of household appliances. Conventional hair dryers, toasters and broilers use nichrome wire coils to achieve high heat levels. Bespoke heating and cutting tools also comprise nichrome coils.